The Technologies
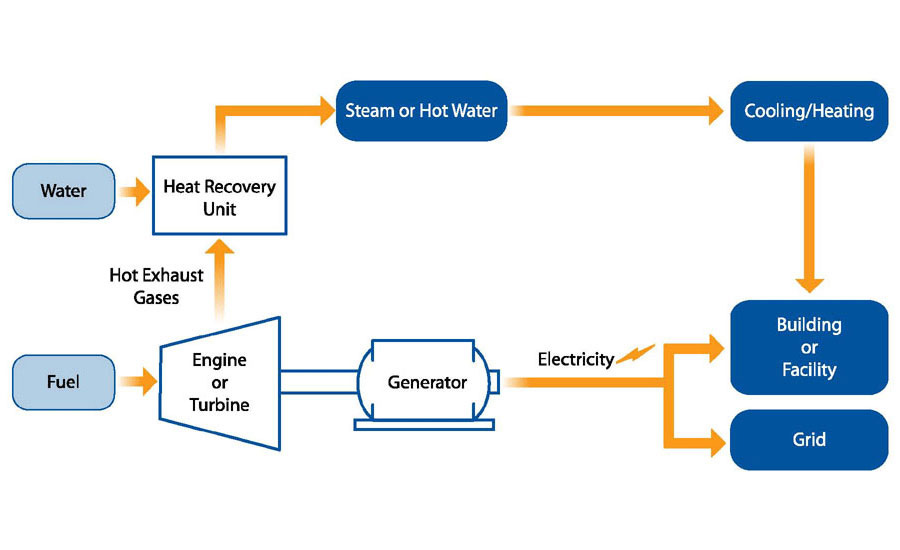
CHP
Combined heat and power (CHP), also known as cogeneration, is the concurrent production of electricity or mechanical power and useful thermal energy (heating and/or cooling) from a single source of energy.
CHP is a type of distributed generation, which, unlike central station generation, is located at or near the point of consumption. CHP employs various technologies that can use a variety of fuels to generate electricity or power at the point of use, allowing the heat that would normally be lost in the power generation process to be recovered to provide needed heating and/or cooling.
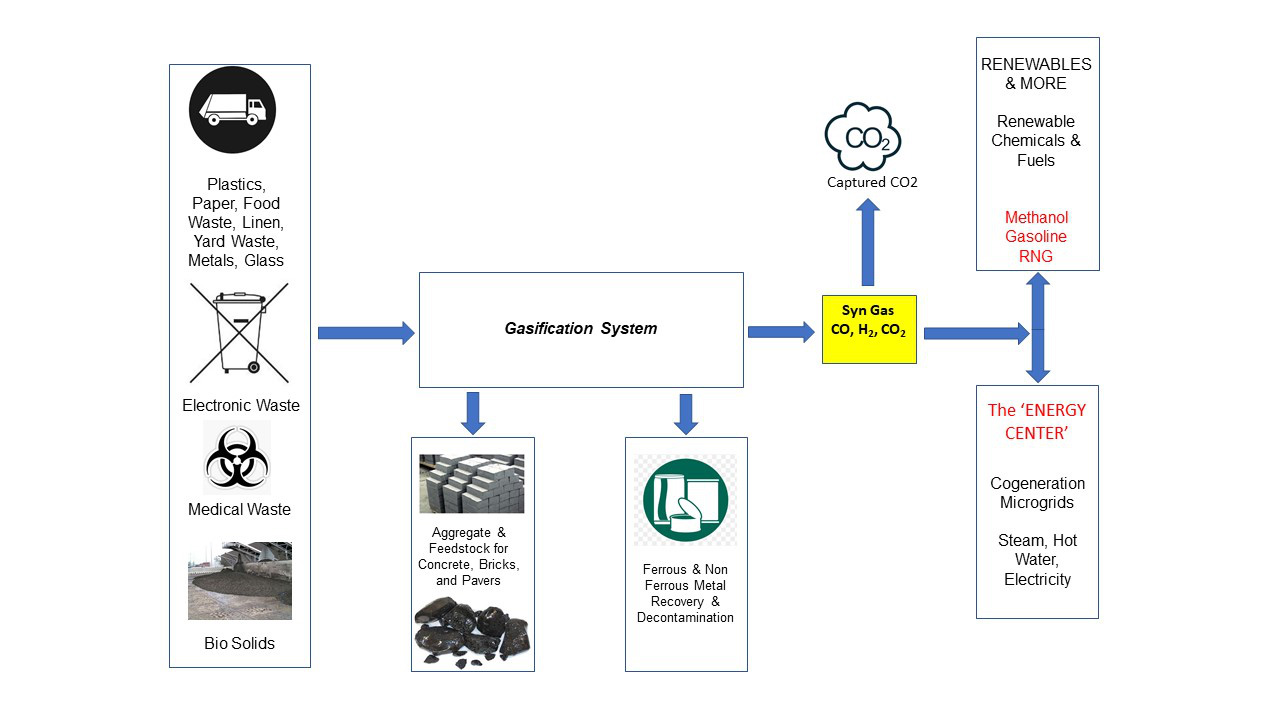
Advanced Recycling
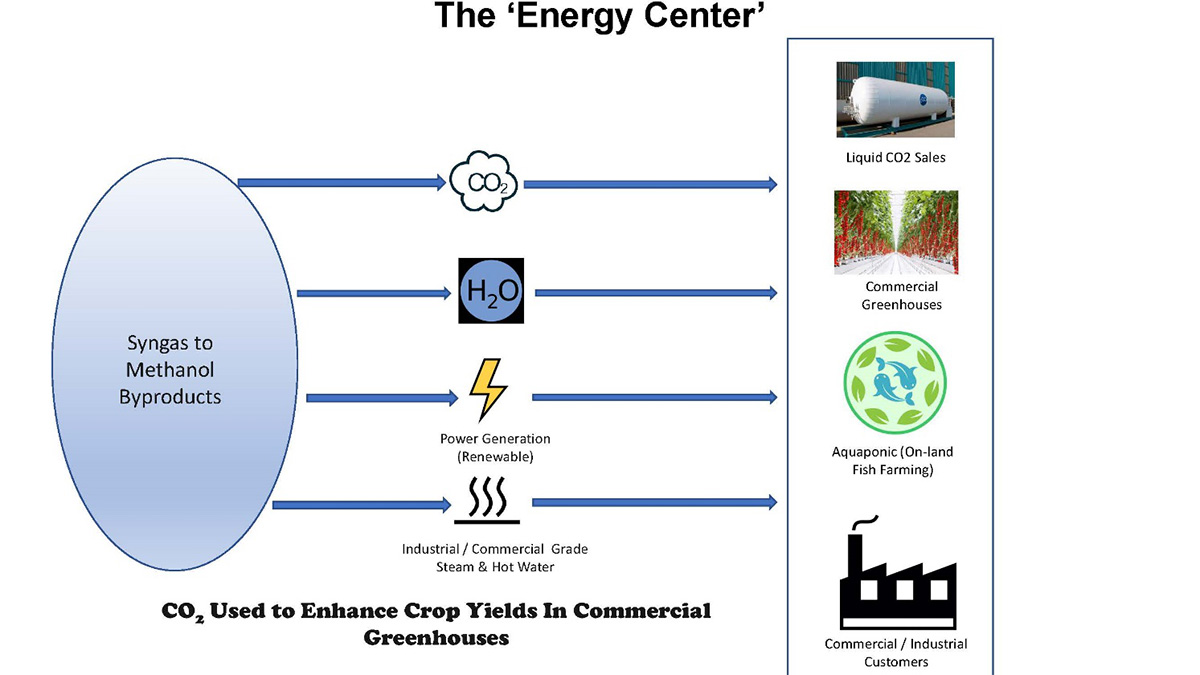
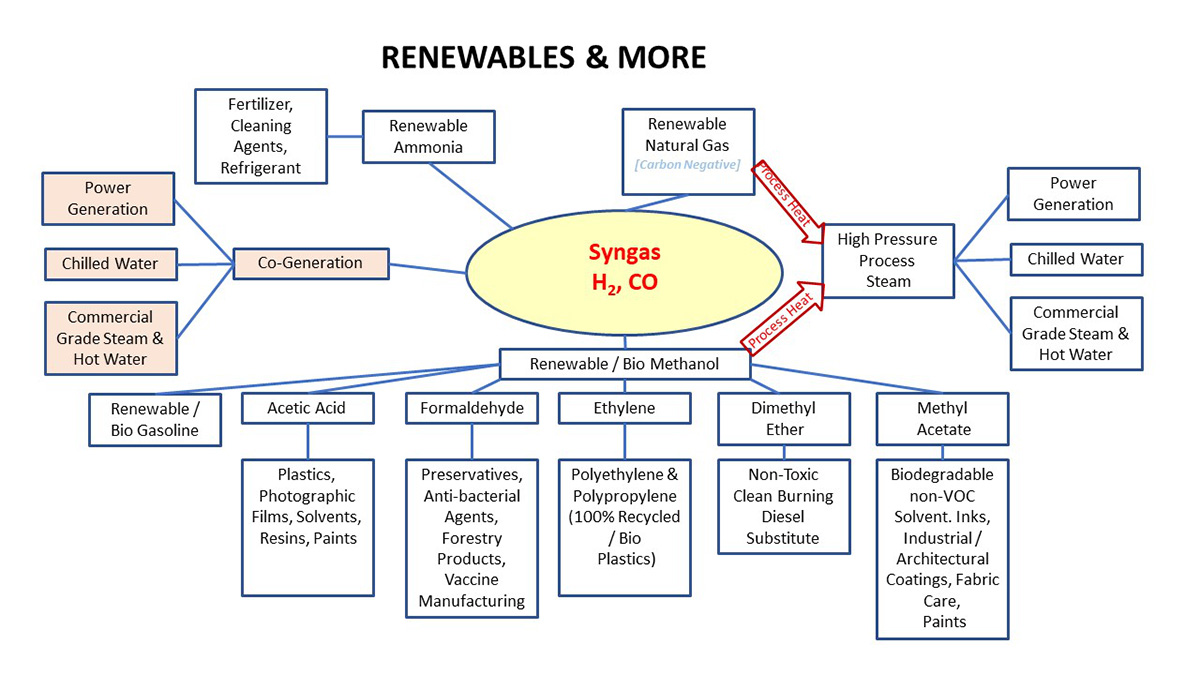
This novel technology offers substantial advantages over conventional recycling systems. Using the organic fractions of a wide variety of feedstocks can be converted to syngas comprised primarily of hydrogen (H2) and carbon monoxide (CO). The syngas, when properly cleaned and conditioned, can be used to generate steam and electricity at higher efficiency than conventional recycling systems.
The transformational leap beyond current recycling systems is the ability to produce byproducts such as liquid fuels, hydrogen, or industrial chemicals from clean syngas. While we will be contributing much needed energy to the grid in the area, we have the option to divert syngas resources to manufacture other valuable products as the market demands.